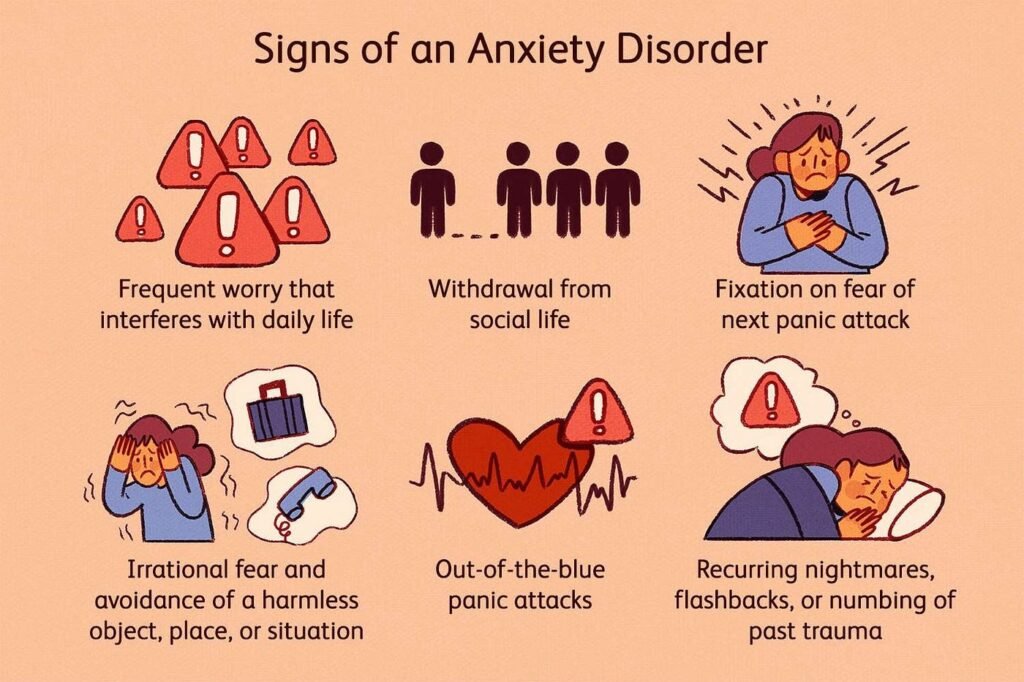
Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions globally, affecting millions of people every year. Anxiety is a natural response to stress, but for some individuals, it becomes more intense, persistent, and overwhelming. This can significantly interfere with daily activities, relationships, and overall quality of life. Understanding the signs and symptoms of anxiety disorders is essential for early detection and proper treatment. In this article, we will explore the various types of anxiety disorders, their symptoms, and when it’s time to seek professional help.
What are Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive worry, fear, or nervousness. These feelings are often disproportionate to the actual situation or event, and they can be overwhelming. Anxiety disorders are not just about feeling stressed or nervous occasionally; they can cause persistent and excessive anxiety that affects a person’s ability to function normally.
There are several types of anxiety disorders, including:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Panic Disorder
- Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
- Specific Phobias
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Each of these conditions has its own set of symptoms, though there is significant overlap. Recognizing these signs and symptoms is crucial for managing and treating anxiety effectively.
General Signs and Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
Regardless of the specific type of anxiety disorder, there are common signs and symptoms that can indicate the presence of an anxiety disorder. These include both physical and emotional manifestations.
1. Constant Worrying
One of the hallmark symptoms of anxiety disorders is constant, excessive worry. This could be worrying about a variety of things, such as health, work, social situations, or relationships. Individuals with anxiety may find it difficult to control their worry, even when there is no specific reason to be concerned.
2. Restlessness or Feeling on Edge
People with anxiety disorders often feel a sense of unease or restlessness. It may feel like being constantly on edge, as if something bad is going to happen, even though there may not be any obvious trigger.
3. Fatigue
Despite worrying excessively, individuals with anxiety may feel mentally and physically drained. The constant state of alertness or unease can cause fatigue and make it difficult to concentrate or enjoy daily activities.
4. Difficulty Concentrating
Anxiety can make it challenging to focus on tasks or even engage in simple conversations. The constant worrying can overwhelm the mind, making it hard to stay focused or complete tasks effectively.
5. Irritability
Excessive anxiety can lead to irritability and mood swings. Even small inconveniences or disruptions can trigger emotional reactions. People with anxiety may feel easily frustrated or upset over minor issues.
6. Muscle Tension
Physically, anxiety can manifest as muscle tension, especially in the neck, shoulders, or back. This tension may lead to discomfort or headaches, further exacerbating feelings of anxiety.
7. Sleep Disturbances
People with anxiety disorders often experience sleep difficulties, including trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or having restless nights. The racing thoughts and worry can interfere with relaxation, making it difficult to achieve a restful night’s sleep.
8. Physical Symptoms
Anxiety disorders can cause a variety of physical symptoms, such as:
- Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Trembling or shaking
These physical symptoms are often mistaken for signs of other health issues, but they are typically a result of the body’s “fight or flight” response triggered by anxiety.
Specific Symptoms of Common Anxiety Disorders
While the general signs and symptoms mentioned above are common across anxiety disorders, each type of anxiety disorder has unique characteristics that make them distinguishable from one another.
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is characterized by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, or family. People with GAD tend to anticipate the worst-case scenario and have difficulty controlling their anxiety. In addition to the common symptoms of anxiety, GAD may also include:
- Chronic nervousness or restlessness
- Difficulty relaxing or sitting still
- Persistent fear of something bad happening
- Overthinking or overanalyzing situations
2. Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder is characterized by recurrent and unexpected panic attacks—intense periods of fear that occur suddenly and without warning. Symptoms of a panic attack include:
- A racing heart or palpitations
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath or a sensation of choking
- Sweating, chills, or hot flashes
- Dizziness or fainting
- Nausea or abdominal distress
- A feeling of impending doom or losing control
Panic attacks can be very frightening and may lead individuals to avoid situations where they fear they might have another attack.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
Social Anxiety Disorder, also known as social phobia, is characterized by an intense fear of being judged or scrutinized by others in social situations. Individuals with SAD often avoid social interactions and may experience significant distress in social settings. Symptoms may include:
- Extreme fear of public speaking or being the center of attention
- Avoidance of social situations or gatherings
- Fear of embarrassment or humiliation
- Physical symptoms like sweating, shaking, or blushing during social interactions
4. Specific Phobias
Specific Phobias are intense, irrational fears of specific objects or situations, such as spiders, heights, flying, or enclosed spaces. Individuals with phobias go to great lengths to avoid the object or situation that triggers their fear. Symptoms can include:
- Immediate and intense fear when exposed to the phobic object or situation
- Physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat or nausea
- Avoidance behavior that interferes with daily life
5. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is characterized by unwanted and intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at reducing anxiety. Common symptoms include:
- Repetitive washing, cleaning, or checking behaviors
- Fear of contamination or harm
- Intrusive, disturbing thoughts that cause distress
- Compulsions performed to alleviate anxiety caused by obsessive thoughts
6. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
PTSD can develop after an individual experiences a traumatic event, such as an accident, assault, or natural disaster. Symptoms include:
- Flashbacks or nightmares related to the traumatic event
- Hypervigilance or being easily startled
- Avoidance of reminders of the trauma
- Difficulty sleeping or concentrating
When to Seek Professional Help
Anxiety can be managed with the right treatment, but it’s essential to seek professional help if anxiety symptoms are overwhelming or persistent. If you notice that anxiety is affecting your ability to function in daily life, or if you experience panic attacks, persistent worry, or physical symptoms, it may be time to consult a mental health professional. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes and prevent the anxiety from worsening.
Conclusion
Anxiety disorders are more than just occasional feelings of stress or nervousness. They are serious mental health conditions that can significantly impact a person’s life. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of anxiety disorders is crucial for seeking timely help and receiving the right treatment. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, don’t hesitate to reach out for professional support. With the right strategies, it’s possible to manage anxiety and improve quality of life.